Categories
AssetPass User Roles
The AssetPass digital inheritance process involves three different user roles.
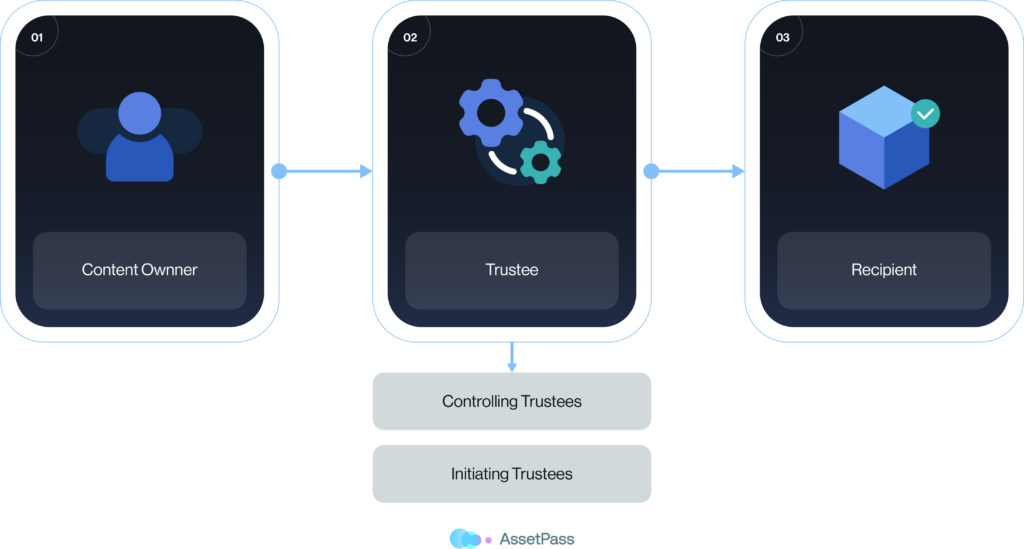
1. Content Owner
The content owner is the individual who wants to create a digital inheritance plan. They do this by creating archives and storing their digital assets in them. They select trustees who will manage the release of the assets when the time is right, and select recipients. Recipients and trustees can be the same.
2. Trustees
Trustees are trusted individuals the Content Owner selects to help secure and deliver their digital assets when the time is right. Trustees do not have access or visibility to the assets stored, but act as facilitators to ensure the your assets are delivered to recipients. Multiple trustees can be appointed for one archive.
There are two types of trustees: Controlling trustees and Initiating trustees.
2.1 Controlling Trustees
Controlling trustees act on the behalf of the content owner when they are not able to respond to release requests. Controlling trustees can approve release requests from Release trustees when the owner is unable to respond after a certain period of time, typically around 30 days. They can be your lawyer or accountant or a very trusted confident.
Additionally they support the content owner, by storing a part of archive security key and help in account recovery scenarios.
2.2 Initiating Trustees
Initiating trustees are trusted friends who know when the time is right to order the release of the archive.
They request the release of the archives, if the Content Owner doesn’t approve the controlling trustees will be automatically contacted to initiate the release.
Additionally they store part of the archive security key on behalf of the owner which is transferred to the Recipient on release approval.
3. Recipients
Recipients are the beneficiaries chosen by the Content Owner to receive their digital legacy. When it is time for the digital assets to be distributed, recipients will receive an email notification informing them that the archive will be available. Beneficiaries can include next of kin, spouses, partners, lawyers, or other designated individuals.